Searching the web has become an essential part of our daily lives, and mastering advanced search techniques can significantly enhance your research capabilities. One of the most powerful tools available is the "INURL" operator, which allows users to search for specific keywords within the URLs of websites. Whether you're a digital marketer, SEO specialist, or simply someone looking to refine your search skills, understanding how to use INURL can open up a world of possibilities.
The INURL operator is a Google search operator that helps you find web pages with specific terms in their URLs. This technique is particularly useful for discovering hidden content, competitor analysis, and uncovering valuable data that might not be immediately visible through standard searches. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to use INURL effectively and responsibly.
In today's data-driven world, knowing how to extract relevant information quickly and efficiently is crucial. Whether you're conducting market research, performing SEO audits, or simply looking for specific types of content, the INURL operator can be a game-changer. Let's dive deeper into how you can harness its power to achieve your goals.
Read also:Online Fifth Third Bank The Ultimate Guide To Banking Services And Features
Table of Contents
- What is INURL?
- How Does INURL Work?
- Basic Syntax of INURL
- Use Cases for INURL
- Combining INURL with Other Operators
- Advanced INURL Techniques
- Ethical Considerations When Using INURL
- Tools to Enhance Your INURL Searches
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
What is INURL?
INURL stands for "in URL," and it is one of the many advanced search operators provided by Google. This operator allows users to search for specific keywords or phrases within the URLs of web pages. Unlike regular searches, which scan the entire content of a page, INURL focuses exclusively on the URL structure, making it an incredibly precise tool for finding targeted information.
For example, if you're looking for pages that contain the word "login" in their URL, you can use the INURL operator to quickly locate all such pages. This is particularly useful for identifying login portals, admin dashboards, or other types of sensitive content that may not be easily discoverable through standard search methods.
It's important to note that while INURL can be a powerful tool, it should always be used responsibly and ethically. Misuse of this operator can lead to unintended consequences, including potential legal issues. Always ensure that your searches are conducted with proper authorization and for legitimate purposes.
How Does INURL Work?
When you use the INURL operator, Google scans the URL structure of indexed web pages for the specified keyword. If the keyword appears in the URL, the page is included in the search results. This process is highly efficient and allows users to pinpoint exact matches with minimal effort.
For instance, if you enter the query "inurl:contact," Google will return a list of web pages where the word "contact" appears in the URL. This could include pages like "example.com/contact-us" or "example.com/contact-support." The INURL operator works by filtering out irrelevant results and focusing solely on URLs that meet the specified criteria.
Understanding how INURL works is essential for maximizing its potential. By combining it with other search operators and refining your queries, you can unlock even more advanced capabilities. Let's explore the basic syntax of INURL to get started.
Read also:Millie Bobby Brown Boyfriend Name A Comprehensive Guide
Basic Syntax of INURL
The basic syntax for using the INURL operator is straightforward. Simply type "inurl:" followed by the keyword or phrase you want to search for. Here's an example:
inurl:register
This query will return all pages where the word "register" appears in the URL. You can also use multiple keywords by separating them with a space:
inurl:login admin
This will search for URLs containing both "login" and "admin." Remember to avoid using quotation marks unless you're searching for an exact phrase. For example:
- inurl:"login page" - This will search for URLs containing the exact phrase "login page."
- inurl:login page - This will search for URLs containing either "login" or "page" or both.
Mastering the basic syntax of INURL is the first step toward becoming proficient in advanced search techniques. As you gain more experience, you can experiment with more complex queries to refine your results further.
Use Cases for INURL
1. SEO Audits
One of the most common use cases for INURL is conducting SEO audits. By searching for specific keywords in URLs, you can identify pages that may need optimization or restructuring. For example, if you're auditing a website for broken links, you can use INURL to find all pages containing the word "error" in their URL:
inurl:error
This will help you quickly locate any error pages and address the underlying issues.
2. Competitor Analysis
INURL is also a valuable tool for competitive analysis. By searching for specific keywords related to your competitors' products or services, you can gain insights into their website structure and content strategy. For instance:
inurl:product-category
This query can help you discover how your competitors organize their product categories and identify potential gaps in your own offerings.
3. Content Discovery
Another useful application of INURL is content discovery. Whether you're looking for blog posts, whitepapers, or case studies, INURL can help you find relevant content more efficiently. For example:
inurl:case-study
This query will return all pages where the phrase "case-study" appears in the URL, allowing you to access valuable resources for your research.
Combining INURL with Other Operators
While INURL is powerful on its own, combining it with other search operators can significantly enhance its capabilities. Here are some examples:
1. Site Operator
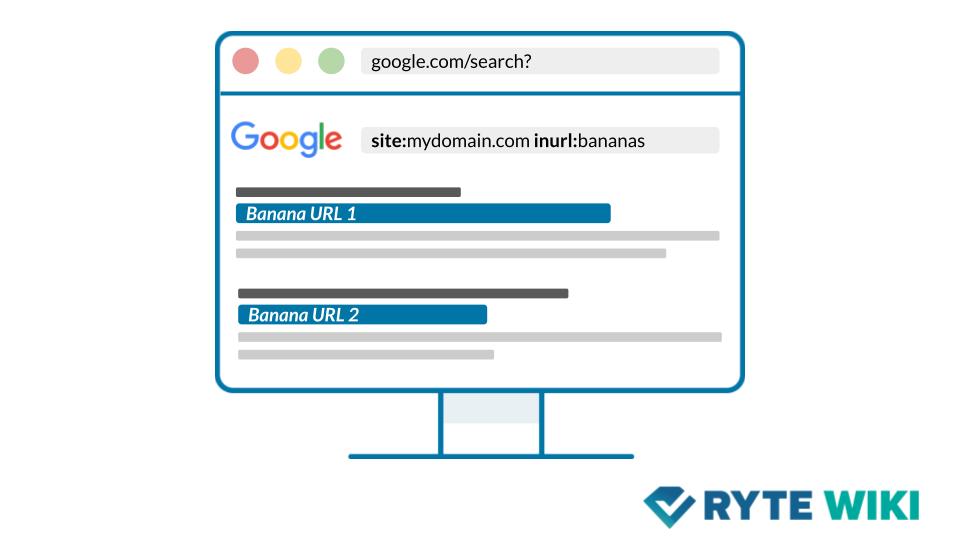
The site operator limits your search to a specific website. By combining it with INURL, you can search for specific keywords within the URLs of a particular domain. For example:
site:example.com inurl:contact
This query will return all pages on example.com where the word "contact" appears in the URL.
2. Filetype Operator
The filetype operator allows you to search for specific file types, such as PDFs or DOCs. When combined with INURL, it can help you locate documents with specific keywords in their URLs. For example:
inurl:report filetype:pdf
This query will find all PDF files where the word "report" appears in the URL.
3. Intext Operator
The intext operator searches for specific keywords within the body of a page. Combining it with INURL allows you to refine your search even further. For example:
inurl:login intext:"forgot password"
This query will find all pages where the word "login" appears in the URL and the phrase "forgot password" appears in the body of the page.
Advanced INURL Techniques
Once you've mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques to take your INURL skills to the next level. Here are a few tips:
- Wildcard Search: Use the asterisk (*) as a wildcard to search for variations of a keyword. For example, inurl:product* will find URLs containing "product" followed by any additional characters.
- Boolean Operators: Use Boolean operators like AND, OR, and NOT to refine your queries. For example, inurl:login AND admin will find pages containing both "login" and "admin" in the URL.
- Exclusion: Use the minus (-) sign to exclude specific keywords from your search. For example, inurl:contact -email will find pages containing "contact" but not "email" in the URL.
Experimenting with these advanced techniques can help you uncover even more valuable insights and refine your search results further.
Ethical Considerations When Using INURL
While INURL is a powerful tool, it's important to use it responsibly and ethically. Misuse of this operator can lead to unintended consequences, including potential legal issues. Here are some guidelines to keep in mind:
- Respect Privacy: Avoid using INURL to access sensitive or private information without proper authorization.
- Follow Legal Guidelines: Ensure that your searches comply with local laws and regulations.
- Use for Legitimate Purposes: Only use INURL for legitimate research, analysis, or troubleshooting purposes.
By adhering to these ethical considerations, you can ensure that your use of INURL remains responsible and productive.
Tools to Enhance Your INURL Searches
There are several tools available that can enhance your INURL searches and make them more efficient. Here are a few worth exploring:
1. Google Advanced Search
Google's advanced search interface allows you to refine your queries using various parameters, including INURL. This can help you save time and improve the accuracy of your searches.
2. SEO Tools
Many SEO tools, such as Ahrefs and SEMrush, offer features that incorporate INURL functionality. These tools can provide additional insights and help you analyze your results more effectively.
3. Browser Extensions
Browser extensions like Search Operators for Google can simplify the process of using INURL and other advanced search operators. These tools often provide one-click access to common operators, making your searches faster and more convenient.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While INURL is a powerful tool, there are a few common mistakes that users often make. Here are some to watch out for:
- Keyword Stuffing: Avoid overusing keywords in your queries, as this can lead to irrelevant or low-quality results.
- Ignoring Context: Always consider the context of your searches to ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant.
- Overlooking Variations: Don't forget to include variations of your keywords to capture a broader range of results.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can improve the effectiveness of your INURL searches and achieve better results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering how to use INURL can significantly enhance your ability to conduct advanced searches and extract valuable information from the web. From SEO audits to competitor analysis, the applications of this powerful operator are virtually limitless. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide and adhering to ethical considerations, you can harness the full potential of INURL to achieve your goals.
We encourage you to experiment with the techniques discussed in this article and share your experiences in the comments below. Your feedback and insights can help others improve their skills and expand their knowledge. Don't forget to explore our other articles for more tips and tricks on mastering advanced search techniques.
Thank you for reading, and happy searching!