Understanding Wisconsin state tax is essential for residents, businesses, and anyone involved in financial transactions within the state. Whether you're filing personal income taxes or managing business expenses, knowing the ins and outs of WI state tax can help you make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Wisconsin taxation, providing you with actionable insights and expert advice.
Taxes play a vital role in funding public services, infrastructure, and education systems. For Wisconsin residents, understanding how state taxes work ensures compliance and maximizes potential savings. This article aims to provide clarity on WI state tax laws, rates, and procedures while addressing common questions and concerns.
Whether you're a new resident, a business owner, or simply seeking to expand your knowledge of Wisconsin's tax system, this guide is designed to offer detailed information and practical tips. Let's explore the key aspects of WI state tax and how it impacts your financial life.
Read also:Kevin Gates Lyrics Really Really A Comprehensive Dive Into The Hit Song
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to WI State Tax
- Key Components of Wisconsin Tax
- WI Income Tax
- Sales and Use Tax
- Property Tax in Wisconsin
- Business Taxes
- Tax Exemptions and Credits
- Filing Your WI State Tax
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Resources and Support
Introduction to WI State Tax
Wisconsin state tax encompasses various forms of taxation designed to generate revenue for public services, infrastructure, and education. These taxes are levied on individuals, businesses, and properties within the state. Understanding the structure and components of WI state tax is crucial for ensuring compliance and optimizing financial planning.
Residents of Wisconsin are subject to several types of taxes, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business taxes. Each tax category has its own set of rules, rates, and filing requirements. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you can better manage your financial responsibilities and take advantage of available tax benefits.
Why is WI State Tax Important?
Taxes collected by the state of Wisconsin fund essential services such as public education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. For individuals and businesses, understanding WI state tax helps in planning finances, avoiding penalties, and maximizing deductions and credits.
Key Components of Wisconsin Tax
The Wisconsin tax system consists of several key components, each serving a specific purpose. These components include income tax, sales tax, property tax, and various business-related taxes. Below, we explore each component in detail:
Income Tax
Wisconsin imposes a progressive income tax system, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. The state uses four tax brackets to determine the amount of tax owed by individuals and families.
Read also:Florida Department Of Nursing A Comprehensive Guide To Advancing Your Nursing Career
Sales Tax
Sales tax in Wisconsin is applied to most retail transactions, with certain exemptions for items like groceries and prescription medications. The state sales tax rate is currently 5%, but local municipalities may impose additional taxes.
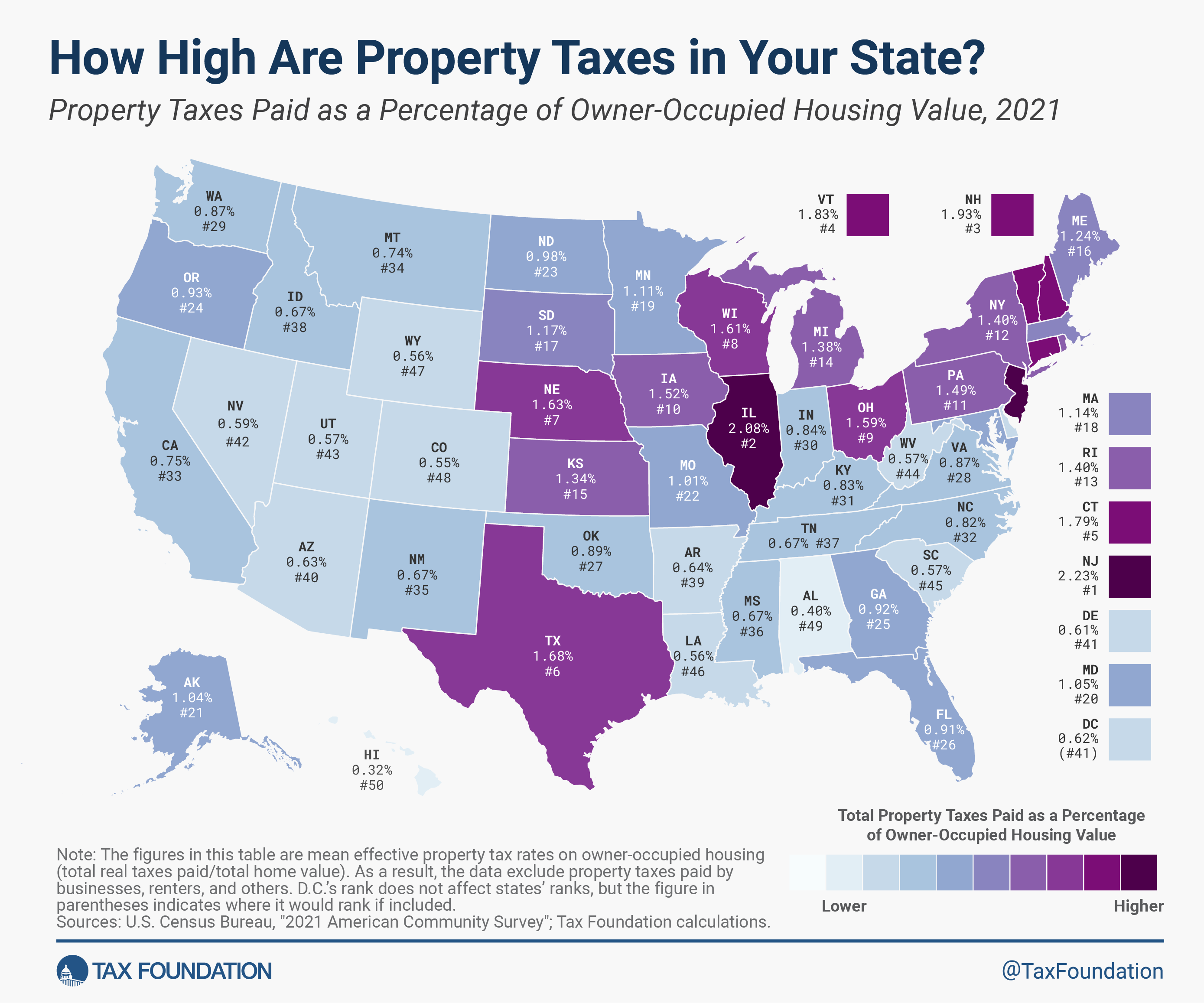
Property Tax
Property taxes in Wisconsin are assessed based on the value of real estate and personal property. These taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments and school districts.
WI Income Tax
Wisconsin income tax is a critical component of the state's tax system. It is calculated based on taxable income and falls under four distinct tax brackets:
- Bracket 1: 4% for income up to $11,850
- Bracket 2: 6.17% for income between $11,851 and $23,700
- Bracket 3: 6.27% for income between $23,701 and $283,250
- Bracket 4: 7.65% for income above $283,251
These brackets ensure that taxpayers are assessed fairly based on their income levels. Additionally, Wisconsin offers various deductions and credits to help reduce taxable income.
How to Calculate WI Income Tax
To calculate your Wisconsin income tax liability, you need to determine your taxable income, apply the appropriate tax brackets, and account for any deductions or credits. Using tax software or consulting a tax professional can simplify this process.
Sales and Use Tax
Sales tax in Wisconsin is levied on most retail purchases, with a standard rate of 5%. However, local municipalities may impose additional sales taxes, raising the total rate in some areas. Certain items, such as groceries and prescription medications, are exempt from sales tax.
Use Tax
Use tax applies to purchases made from out-of-state retailers where sales tax was not collected. Wisconsin residents are responsible for reporting and paying use tax on these purchases. This ensures that the state receives its fair share of revenue from all taxable transactions.
Property Tax in Wisconsin
Property taxes in Wisconsin are assessed based on the assessed value of real estate and personal property. These taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments and school districts. Property tax rates vary by municipality, depending on local needs and budgets.
Assessment Process
The property assessment process involves determining the market value of a property and applying the appropriate tax rate. Property owners receive annual assessments and have the opportunity to appeal if they believe the valuation is inaccurate.
Business Taxes
Businesses operating in Wisconsin are subject to various taxes, including income tax, franchise tax, and excise tax. These taxes are designed to ensure that businesses contribute fairly to the state's revenue generation efforts.
Income Tax for Businesses
Businesses in Wisconsin are required to file income tax returns and pay taxes on their net income. The tax rates vary depending on the type of business entity and its income level.
Tax Exemptions and Credits
Wisconsin offers several tax exemptions and credits to help reduce the tax burden on individuals and businesses. These include exemptions for certain purchases, credits for education expenses, and incentives for renewable energy investments.
Common Tax Credits
- Homestead Credit: Provides relief to low- and middle-income homeowners and renters.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit: Offers tax relief for expenses related to child care and dependent care.
- Energy Efficiency Credit: Encourages investments in energy-efficient home improvements.
Filing Your WI State Tax
Filing your Wisconsin state tax return is a straightforward process, especially with the help of tax software or a qualified tax professional. The deadline for filing is typically April 15th, although extensions may be granted under certain circumstances.
Steps to File
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2 forms, 1099s, and receipts for deductions and credits.
- Use tax software or consult a tax professional to prepare your return.
- Submit your return electronically or by mail before the deadline.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common tax filing mistakes can save you time, money, and potential penalties. Some common errors include failing to report all sources of income, missing deadlines, and overlooking available deductions and credits.
Tips for Avoiding Mistakes
- Double-check all calculations and entries before submitting your return.
- Consult a tax professional if you're unsure about any aspect of the filing process.
- Stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations.
Resources and Support
Several resources are available to help you navigate the complexities of Wisconsin state tax. The Wisconsin Department of Revenue offers comprehensive guides, FAQs, and contact information for assistance. Additionally, tax professionals and software programs can provide valuable support.
Where to Find Help
- Wisconsin Department of Revenue website
- Local tax professionals and accountants
- Tax preparation software and online resources
Kesimpulan
In summary, understanding what is WI state tax is essential for residents, businesses, and anyone involved in financial transactions within the state. By familiarizing yourself with the various components of Wisconsin taxation, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business taxes, you can ensure compliance and maximize potential savings.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax situation, consulting available resources, and seeking professional advice if needed. Don't forget to share this article with others who may benefit from the information, and feel free to leave a comment or question below. Thank you for reading, and best of luck with your tax planning!
For further reading, explore our other articles on financial management, tax strategies, and personal finance tips. Stay informed and empowered in managing your financial future!
Sources:
- Wisconsin Department of Revenue
- IRS Publication 553
- State Tax Handbook